
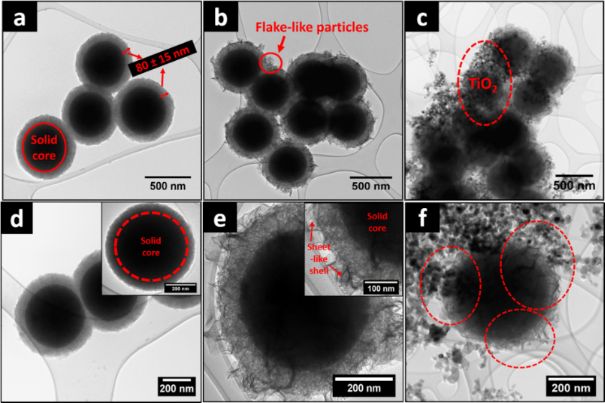
The increase of Jsc is attributed to the enhanced dye light absorption in strength and spectral range due to the surface plasmon resonance of AgNPs in photo anode. The improvement is manifested chiefly as an increase in photocurrent density due to enhanced light harvesting by the silver nanoparticles (AgNPs). The plasmonic effect as observed by introducing in DSSC produces higher performance with short-circuitcurrent density (JSC) of 0.178 mAcm-2, open-circuit voltage (VOC) of 0.470 V, fill factor (FF) of0.554, yielding an efficiency (η) of 0.046%. The SiO2 nanospheres were used as a support to prevent the. In this study, a novel ternary heterostructure pholocatalyst, ZnIn2S4SiO2TiO2 (ZISSiO2TiO2) was successfully prepared by simple solgel and solvothermal methods. The efficiency of betalain dye sensitized solar cell (0.009 %) increased to 0.046 % upon deployment of and to 0.024 % upon incorporation of nanoparticles. It is challenging to design and prepare difunctional photocatalysts for simultaneous photocatalytic wastewater purification and hydrogen (H2) energy production. The performance of plasmon assisted dye sensitized solar cells capped with SiO2 and TiO2 was investigated. Metal nanoparticles are playing important role in photovoltaic and photocatalytic action of semiconductor nanostructures either through Fermi level shift or introducing localized surface plasmon effects. Transasctions of NAMP VOL4 (July, 2017).Savinov, Photocatalytic methods of water and air purification, Sorosovskij obrazovatel'nyj zhurnal 6 (11) (2000) 52‒56. Fe 3 O 4 /TiO 2 core/shell nanoparticles as affinity probes for the analysis of phosphopeptides using TiO 2 surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Magnetic photocatalyst / Hiroshi F., Yukiko H., Michichiro Y. The photodegradation dynamics revealed that even though the oxidation rate decreases over time, about 90% of methyl orange is oxidized during the first 35 min. The photocatalytic activity of Fe 3O SiO 2 nanoparticles was investigated by photodegradation of methyl orange in aqueous solution under UV light irradiation. The resulting particles were separated using a magnet, washed and dried to constant weight, the yield was 70%. Finally, solution of tetrabutoxytitanium was added dropwise to the mixture of Fe 3O 2 nanoparticles under sonication & intense stirring. Secondly, the magnetite nanoparticles were dispersed in ethanol using sonication, and solutions of both ammonia and tetraethoxysilane were added to the suspension under intense stirring, since it was suggested that the introduction of an intermediate passive SiO 2 layer between the Fe 3O 4 and TiO 2 phases inhibits the direct electrical contact and hence prevents the photodissolution of the magnetite phase and deterioration of the surface photocatalytic properties. The fabricated core-shell nanospheres were used for the photodegradation of binary azo dyes in aqueous solution, methyl orange and methylene dyes under UV irradiation light. First the nuclei of magnetite nanoparticles were prepared by co-precipitation of iron (II&III) salts solutions. In this work, the nanosized magnetic Fe 3O 2 photocatalyst was prepared by sol-gel methods.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
